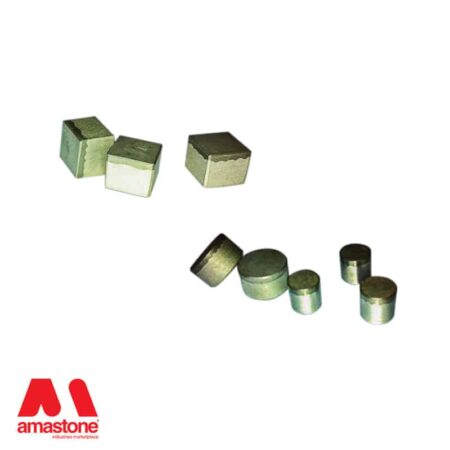
Industrial applications involving the cutting, turning and crushing of “hard” materials require tools made of “exceptionally hard” materials, of high hardness and high resistance to cutting temperatures.
If you work in the field of metal processing or stone processing you will surely have heard about carbide tools, tools in Widia and tools in Polycrystalline (PCD).
Let’s try to understand what is meant by these terms and to make some clarity on the meanings of these terms.
What are hard metals and what is Widia?
There are various types of hard metals, but the best known in the metalworking and stone processing sectors is cemented tungsten carbide, also known as Widia.
The Widia is the name registered by the company Krupp who invented the carbide in 1926. Widia stands for the initials of WIe DIAmant which means “like the diamond”.
Cemented tungsten carbide is nothing but sintered** tungsten carbide with a cobalt metal matrix.
There are other types of hard metals that use not tungsten carbides but titanium carbides or tantalum carbides. For example, Cermet is a material composed of sintered titanium carbide with a nickel metal matrix.
Carbide tools are harder than steel-fast or super-steel and are more resistant to high cutting temperatures. In this way, the carbide tools allow faster machining speeds.
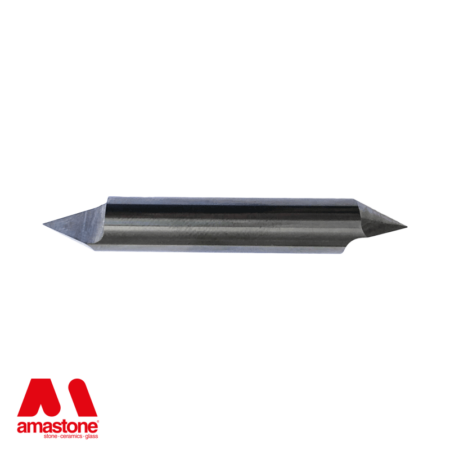
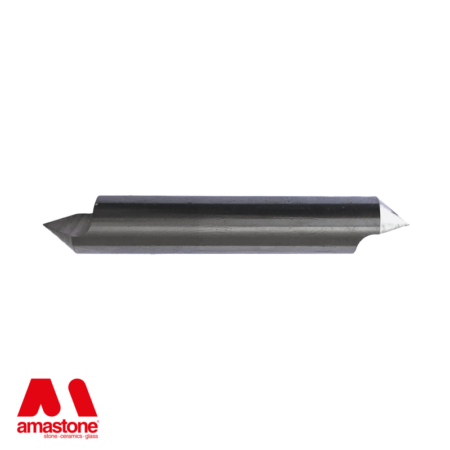
In the processing of marble, widia tools are widely used and have an affordable cost.
For example, the CNC router bits for letter engraving and the finishing of the bas-reliefs are Widia cutters.
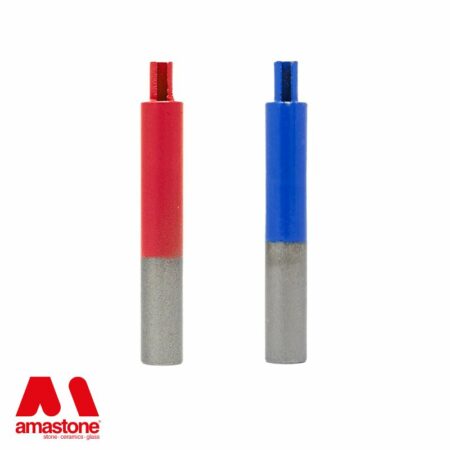
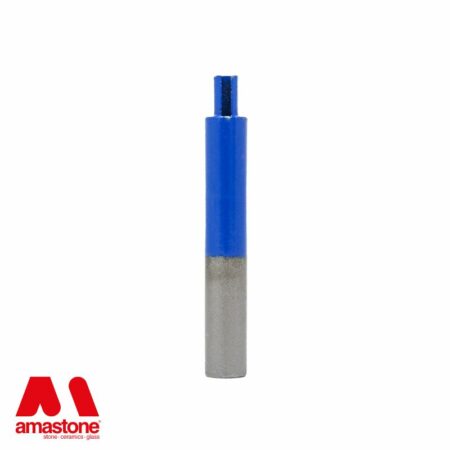
Drill bits for stone and marble drilling are also widia tools
Widia Router bits for marble
Widia Drill bits
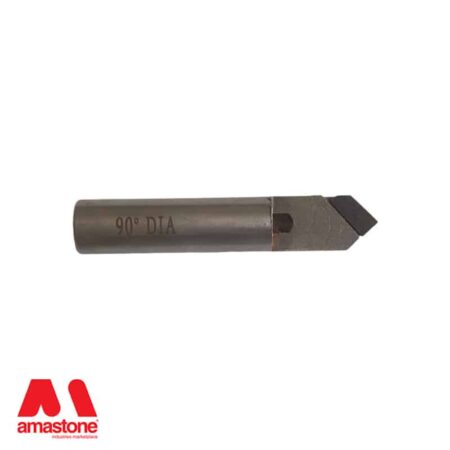
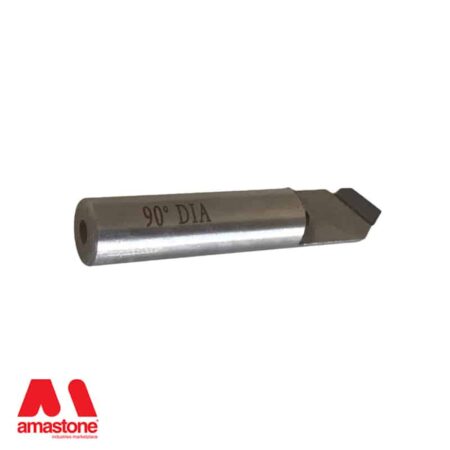
When the carbide is not enough, then it is necessary to switch to polycrystalline bits – PCD Polycrystalline Diamond.
Diamond, both natural and synthetic, is the hardest material in nature and very resistant to abrasion. For this reason, at the industrial level, the PCD finds various applications and is used as a tool cutter to remove, cut, shape and polish hard, but exclusively non-ferrous materials.
What is the Polycrystalline or PCD?
PCD is a synthetic diamond produced through a sintering process ** of diamond crystals with a metal binder.
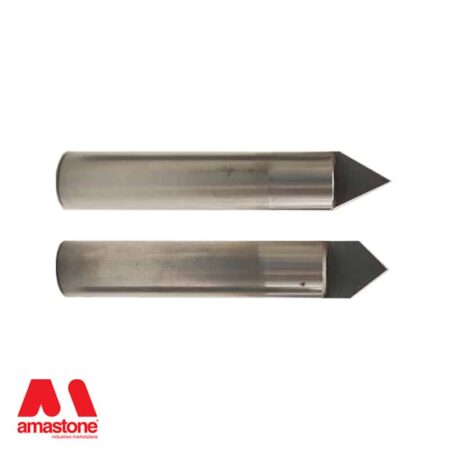
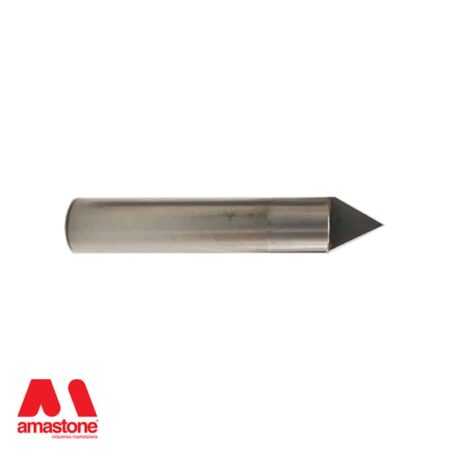
In the stone processing sector, polycrystalline tools are used to process hard materials such as granite, basalt, and quartz.
In order to process such hard and abrasive materials, carbide tools are not suitable because their wear resistance is not sufficient, so the tools are damaged, broken or have a very short duration.
Polycrystalline tools for CNC machines are used for etching on black granite and for the finishing of bas-reliefs in granite and hard stones.
The polycrystalline cutting edges are braze-like plates similar to the widia but black ones.
The life of a polycrystalline milling cutter, if used for example on granite, is 20 times higher than a similar carbide tool. Obviously, the costs of a PCD tool are higher compared to the widia ones
** What is a sintering process?
Sintering is a treatment that transforms powdery materials into indivisible materials. The sintering, therefore, consists in mixing the powdered components (for the widia they would be tungsten carbide + cobalt), pressing them and then heating them under high pressure so that the powders unite to form a single indivisible piece and the desired mechanical and physical characteristics.
The diamond tools used in industry and crafts are obviously not made entirely of hard metal, widia or polycrystalline. A drill bit, or a CNC router bit, is composed of a steel body and a cutting part composed of a hard metal or PCD plate that is mechanically fixed, glued or braze-welded (braze-welded).

 Diamond Blades
Diamond Blades Angle Grinder Tools
Angle Grinder Tools Polishing Machine Tools for Stone, Marble and Granite
Polishing Machine Tools for Stone, Marble and Granite Texture tooling
Texture tooling Adhesives and glue
Adhesives and glue Ceramic, Granite and Marble Drill Bits
Ceramic, Granite and Marble Drill Bits Sculpture – Stone carving tools
Sculpture – Stone carving tools Diamond Wires for Granite and Marble Quarries
Diamond Wires for Granite and Marble Quarries Cemetery and Graveyard Accessories
Cemetery and Graveyard Accessories CNC Vacuum Pods
CNC Vacuum Pods CNC Tool Holders
CNC Tool Holders CNC Tool Forks
CNC Tool Forks Positioning Alignment Lasers
Positioning Alignment Lasers Material Handling
Material Handling Machinery
Machinery Spare parts
Spare parts Electrical Spare Parts
Electrical Spare Parts Personal Protective Equipment
Personal Protective Equipment